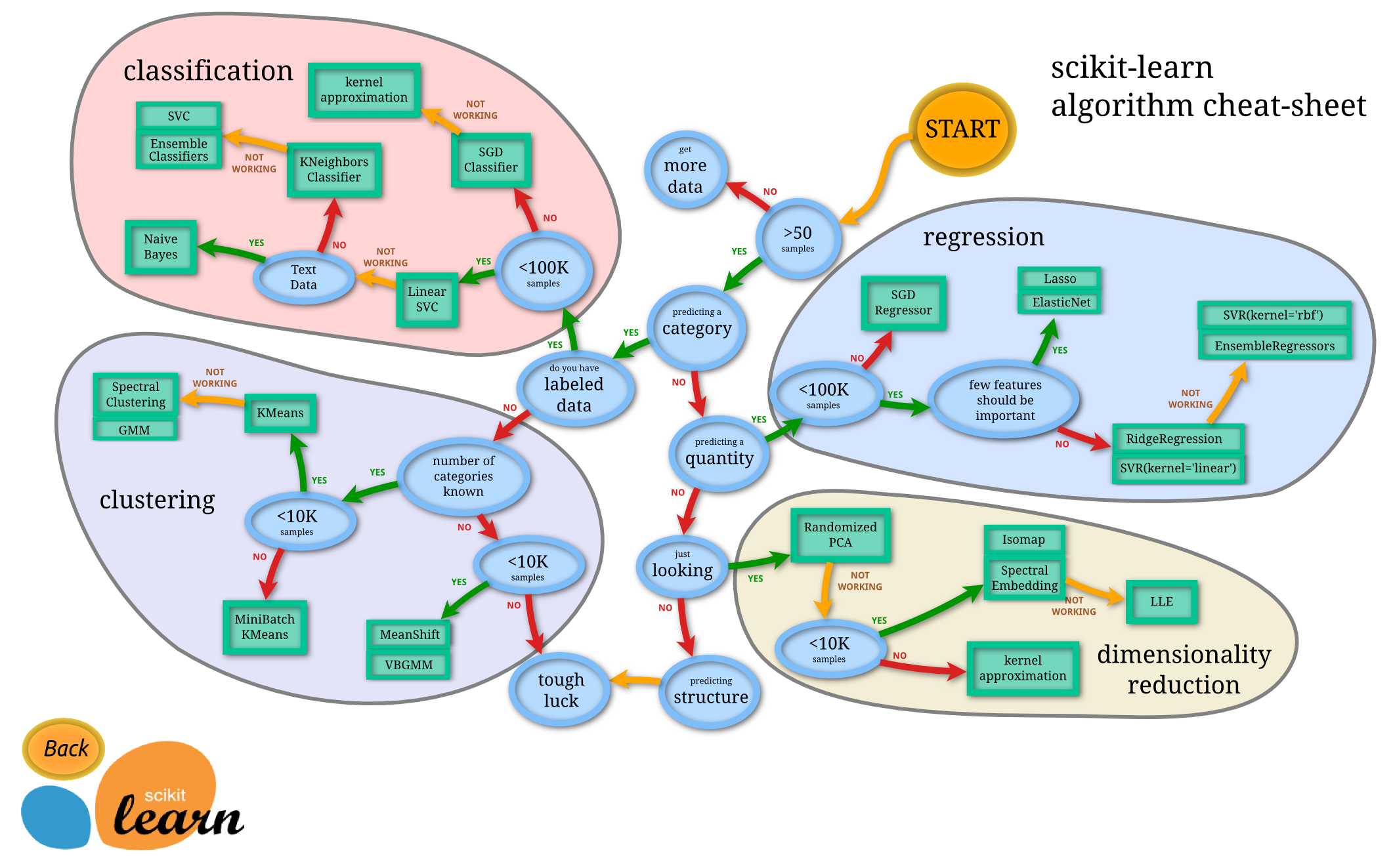
Scikit-Learn

Scikit-learn is an open source Python library that implements a range of machine learning, preprocessing, cross-validation and visualization algorithms using a unified interface.
Install and import Scikit-Learn
$ pip install scikit-learn
Scikit-learn Example
from sklearn import neighbors, datasets, preprocessing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Load the Iris dataset
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Split the dataset into features (X) and target (y)
X, y = iris.data[:, :2], iris.target
# Split the dataset into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=33)
# Standardize the features using StandardScaler
scaler = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit(X_train)
X_train = scaler.transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Create a K-Nearest Neighbors classifier
knn = neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
# Train the classifier on the training data
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict the target values on the test data
y_pred = knn.predict(X_test)
# Calculate the accuracy of the classifier
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
# Print the accuracy
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
Accuracy: 0.631578947368421
Loading The Data
from sklearn import datasets
# Load the Iris dataset
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Split the dataset into features (X) and target (y)
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
# Print the lengths of X and y
print("Size of X:", X.shape) # (150, 4)
print("Size of y:", y.shape) # (150, )
Size of X: (150, 4)
Size of y: (150,)
Training And Test Data
# Import train_test_split from sklearn
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Split the data into training and test sets with test_size=0.2 (20% for test set)
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# Print the sizes of the arrays
print("Size of X_train:", X_train.shape)
print("Size of X_test: ", X_test.shape)
print("Size of y_train:", y_train.shape)
print("Size of y_test: ", y_test.shape)
Size of X_train: (120, 4)
Size of X_test: (30, 4)
Size of y_train: (120,)
Size of y_test: (30,)
Create instances of the models
# Import necessary classes from sklearn libraries
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# Create instances of supervised learning models
# Logistic Regression classifier (max_iter=1000)
lr = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
# k-Nearest Neighbors classifier with 5 neighbors
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
# Support Vector Machine classifier
svc = SVC()
# Create instances of unsupervised learning models
# k-Means clustering with 3 clusters and 10 initialization attempts
k_means = KMeans(n_clusters=3, n_init=10)
# Principal Component Analysis with 2 components
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
Model Fitting
# Fit models to the data
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
svc.fit(X_train, y_train)
k_means.fit(X_train)
pca.fit_transform(X_train)
# Print the instances and models
print("lr:", lr)
print("knn:", knn)
print("svc:", svc)
print("k_means:", k_means)
print("pca:", pca)
lr: LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
knn: KNeighborsClassifier()
svc: SVC()
k_means: KMeans(n_clusters=3, n_init=10)
pca: PCA(n_components=2)
Prediction
# Predict using different supervised estimators
y_pred_svc = svc.predict(X_test)
y_pred_lr = lr.predict(X_test)
y_pred_knn_proba = knn.predict_proba(X_test)
# Predict labels using KMeans in clustering algorithms
y_pred_kmeans = k_means.predict(X_test)
# Print the results
print("Supervised Estimators:")
print("SVC predictions:", y_pred_svc)
print("Logistic Regression predictions:", y_pred_lr)
print("KNeighborsClassifier probabilities:\n", y_pred_knn_proba[:5],"\n ...")
print("\nUnsupervised Estimators:")
print("KMeans predictions:", y_pred_kmeans)
Supervised Estimators:
SVC predictions: [2 1 0 2 0 2 0 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 1 0]
Logistic Regression predictions: [2 1 0 2 0 2 0 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 1 0]
KNeighborsClassifier probabilities:
[[0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 0.]]
...
Unsupervised Estimators:
KMeans predictions: [2 2 0 1 0 1 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 0 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 0 0 2 2 0]
Preprocessing The Data
Standardization
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# Create an instance of the StandardScaler and fit it to training data
scaler = StandardScaler().fit(X_train)
# Transform the training and test data using the scaler
standardized_X = scaler.transform(X_train)
standardized_X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Print the variables
print("\nStandardized X_train:\n", standardized_X[:5],"\n ...")
print("\nStandardized X_test:\n", standardized_X_test[:5],"\n ...")
Standardized X_train:
[[ 0.61303014 0.10850105 0.94751783 0.736072 ]
[-0.56776627 -0.12400121 0.38491447 0.34752959]
[-0.80392556 1.03851009 -1.30289562 -1.33615415]
[ 0.25879121 -0.12400121 0.60995581 0.736072 ]
[ 0.61303014 -0.58900572 1.00377816 1.25412853]]
...
Standardized X_test:
[[-0.09544771 -0.58900572 0.72247648 1.5131568 ]
[ 0.14071157 -1.98401928 0.10361279 -0.30004108]
[-0.44968663 2.66602591 -1.35915595 -1.33615415]
[ 1.6757469 -0.35650346 1.39760052 0.736072 ]
[-1.04008484 0.80600783 -1.30289562 -1.33615415]]
...
Normalization
from sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer
scaler = Normalizer().fit(X_train)
normalized_X = scaler.transform(X_train)
normalized_X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# Print the variables
print("\nNormalized X_train:\n", normalized_X[:5],"\n ...")
print("\nNormalized X_test:\n", normalized_X_test[:5],"\n ...")
Normalized X_train:
[[0.69804799 0.338117 0.59988499 0.196326 ]
[0.69333409 0.38518561 0.57777841 0.1925928 ]
[0.80641965 0.54278246 0.23262105 0.03101614]
[0.71171214 0.35002236 0.57170319 0.21001342]
[0.69417747 0.30370264 0.60740528 0.2386235 ]]
...
Normalized X_test:
[[0.67767924 0.32715549 0.59589036 0.28041899]
[0.78892752 0.28927343 0.52595168 0.13148792]
[0.77867447 0.59462414 0.19820805 0.02831544]
[0.71366557 0.28351098 0.61590317 0.17597233]
[0.80218492 0.54548574 0.24065548 0.0320874 ]]
...
Binarization
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import Binarizer
# Create a sample data array
data = np.array([[1.5, 2.7, 0.8],
[0.2, 3.9, 1.2],
[4.1, 1.0, 2.5]])
# Create a Binarizer instance with a threshold of 2.0
binarizer = Binarizer(threshold=2.0)
# Apply binarization to the data
binarized_data = binarizer.transform(data)
print("Original data:")
print(data)
print("\nBinarized data:")
print(binarized_data)
Original data:
[[1.5 2.7 0.8]
[0.2 3.9 1.2]
[4.1 1. 2.5]]
Binarized data:
[[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 1.]]
Encoding Categorical Features
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
# Sample data: categorical labels
labels = ['cat', 'dog', 'dog', 'fish', 'cat', 'dog', 'fish']
# Create a LabelEncoder instance
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
# Fit and transform the labels
encoded_labels = label_encoder.fit_transform(labels)
# Print the original labels and their encoded versions
print("Original labels:", labels)
print("Encoded labels:", encoded_labels)
# Decode the encoded labels back to the original labels
decoded_labels = label_encoder.inverse_transform(encoded_labels)
print("Decoded labels:", decoded_labels)
Original labels: ['cat', 'dog', 'dog', 'fish', 'cat', 'dog', 'fish']
Encoded labels: [0 1 1 2 0 1 2]
Decoded labels: ['cat' 'dog' 'dog' 'fish' 'cat' 'dog' 'fish']
Imputing Missing Values
import numpy as np
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
# Sample data with missing values
data = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, np.nan],
[4.0, np.nan, 6.0],
[7.0, 8.0, 9.0]])
# Create a SimpleImputer instance with strategy='mean'
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='mean')
# Fit and transform the imputer on the data
imputed_data = imputer.fit_transform(data)
print("Original data:")
print(data)
print("\nImputed data:")
print(imputed_data)
Original data:
[[ 1. 2. nan]
[ 4. nan 6.]
[ 7. 8. 9.]]
Imputed data:
[[1. 2. 7.5]
[4. 5. 6. ]
[7. 8. 9. ]]
Generating Polynomial Features
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
# Sample data
data = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
# Create a PolynomialFeatures instance of degree 2
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
# Transform the data to include polynomial features
poly_data = poly.fit_transform(data)
print("Original data:")
print(data)
print("\nPolynomial features:")
print(poly_data)
Original data:
[[1 2]
[3 4]
[5 6]]
Polynomial features:
[[ 1. 1. 2. 1. 2. 4.]
[ 1. 3. 4. 9. 12. 16.]
[ 1. 5. 6. 25. 30. 36.]]
Classification Metrics
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, confusion_matrix
# Accuracy Score
accuracy_knn = knn.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Accuracy Score (knn):", knn.score(X_test, y_test))
accuracy_y_pred = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_lr)
print("Accuracy Score (y_pred):", accuracy_y_pred)
# Classification Report
classification_rep_y_pred = classification_report(y_test, y_pred_lr)
print("Classification Report (y_pred):\n", classification_rep_y_pred)
classification_rep_y_pred_lr = classification_report(y_test, y_pred_lr)
print("Classification Report (y_pred_lr):\n", classification_rep_y_pred_lr)
# Confusion Matrix
conf_matrix_y_pred_lr = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred_lr)
print("Confusion Matrix (y_pred_lr):\n", conf_matrix_y_pred_lr)
Accuracy Score (knn): 0.9666666666666667
Accuracy Score (y_pred): 1.0
Classification Report (y_pred):
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 11
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 13
2 1.00 1.00 1.00 6
accuracy 1.00 30
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 30
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 30
Classification Report (y_pred_lr):
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 11
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 13
2 1.00 1.00 1.00 6
accuracy 1.00 30
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 30
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 30
Confusion Matrix (y_pred_lr):
[[11 0 0]
[ 0 13 0]
[ 0 0 6]]
Regression Metrics
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error, r2_score
# True values (ground truth)
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2]
# Predicted values
y_pred = [2.8, -0.3, 1.8]
# Calculate Mean Absolute Error
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred)
print("Mean Absolute Error:", mae)
# Calculate Mean Squared Error
mse = mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)
# Calculate R² Score
r2 = r2_score(y_true, y_pred)
print("R² Score:", r2)
Mean Absolute Error: 0.20000000000000004
Mean Squared Error: 0.040000000000000015
R² Score: 0.9815384615384616
Clustering Metrics
from sklearn.metrics import adjusted_rand_score, homogeneity_score, v_measure_score
# Adjusted Rand Index
adjusted_rand_index = adjusted_rand_score(y_test, y_pred_kmeans)
print("Adjusted Rand Index:", adjusted_rand_index)
# Homogeneity Score
homogeneity = homogeneity_score(y_test, y_pred_kmeans)
print("Homogeneity Score:", homogeneity)
# V-Measure Score
v_measure = v_measure_score(y_test, y_pred_kmeans)
print("V-Measure Score:", v_measure)
Adjusted Rand Index: 0.7657144139494176
Homogeneity Score: 0.7553796021571243
V-Measure Score: 0.8005552543570766
Cross-Validation
# Import necessary library
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
# Cross-validation with KNN estimator
knn_scores = cross_val_score(knn, X_train, y_train, cv=4)
print(knn_scores)
# Cross-validation with Linear Regression estimator
lr_scores = cross_val_score(lr, X, y, cv=2)
print(lr_scores)
[0.96666667 0.93333333 1. 0.93333333]
[0.96 0.96]
Grid Search
# Import necessary library
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# Define parameter grid
params = {
'n_neighbors': np.arange(1, 3),
'weights': ['uniform', 'distance']
}
# Create GridSearchCV object
grid = GridSearchCV(estimator=knn, param_grid=params)
# Fit the grid to the data
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Print the best parameters found
print("Best parameters:", grid.best_params_)
# Print the best cross-validation score
print("Best cross-validation score:", grid.best_score_)
# Print the accuracy on the test set using the best parameters
best_knn = grid.best_estimator_
test_accuracy = best_knn.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Test set accuracy:", test_accuracy)
Best parameters: {'n_neighbors': 1, 'weights': 'uniform'}
Best cross-validation score: 0.9416666666666667
Test set accuracy: 1.0